 KnightTour [骑士巡逻]
KnightTour [骑士巡逻]
# 介绍
骑士巡逻(英语:Knight's tour)是指在按照国际象棋中骑士的规定走法走遍整个棋盘的每一个方格,而且每个网格只能够经过一次。假若骑士能够从走回到最初位置,则称此巡逻为 “封闭巡逻”,否则,称为 “开巡逻”。对于 8*8 棋盘,一共有 26,534,728,821,064 种封闭巡逻,有 19,591,828,170,979,904 种开巡逻。
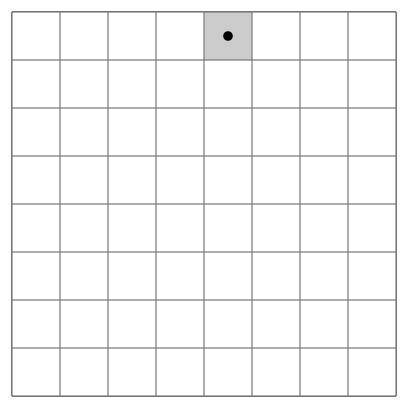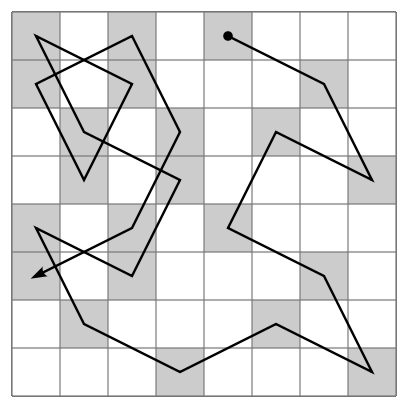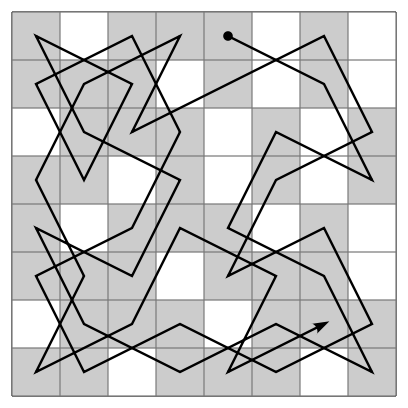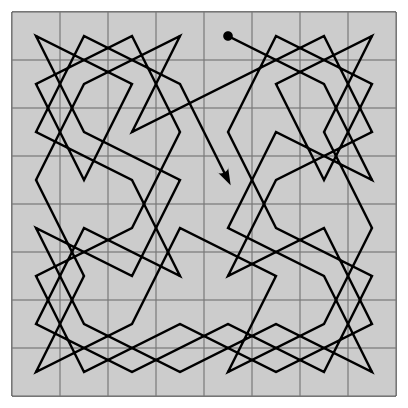
由骑士巡逻引申出了一个著名的数学问题 :骑士巡逻问题 -- 找出所有的骑士巡逻路径。骑士巡逻问题的变种包括各种尺寸的棋盘甚至非正方形的棋盘。
Cull 和 Conrad 证明了对于任何一个 m×n(5<=m<=n)棋盘,至少有一个(可能是开巡逻)骑士巡逻路径。
Schwenk 证明了,除了以下 3 种情况外,任何的 m×n(m<=n)棋盘都至少有 1 个闭巡逻。
- m 和 n 都为奇数
- m= 1, 2, 4
- m= 3 且 n= 4, 6, 8
# 实质
骑士巡逻问题实际上是哈密顿路径问题的一种特殊形式,寻找骑士巡逻的闭巡逻路径的个数实际上也是哈密顿循环问题的一种特殊形式。但是和一般的哈密顿路径问题不同,骑士巡逻问题可以在线性时间内解决。
哈密顿路径问题
图论中的经典问题哈密顿路径问题(台湾作汉米顿路径问题)(Hamiltonian path problem)与哈密顿环问题(台湾作汉米顿环问题)(Hamiltonian cycle problem)分别是来确定在一个给定的图上是否存在哈密顿路径(一条经过图上每个顶点的路径)和哈密顿环(一条经过图上每个顶点的环)。两个问题皆为 NP 完全。
# 解决方法
借助计算机的帮助,人们已经发现了很多种寻找骑士巡逻路径的方法。其中一部分依靠算法,而另外一些则依靠启发法。
- 穷举法:用穷举法来寻找骑士巡逻路径适用于格数较小的棋盘,因为当方格数过多时,可能的路径过多。例如,8×8 棋盘中大约有 4×10^51 种可能的路径。如此大的运算量已经超出了现代计算机的运算能力。
- 分治法:利用分治法将棋盘分成很多小块,计算出每一小块中的所有可能路径,然后将这些小块合并再计算所有可能的路径。
- 人工神经网络方法:骑士巡逻问题同样可以使用人工神经网络来解决。
- Warnsdorff 规则:Warnsdorff 规则指在所有可走且未经过的方格中,马只可能走这样一个方格:从该方格出发,马能跳的方格数最少;如果可跳的方格数相等,则从当前位置看,方格序号小的优先。依照这一规则往往可以找到一条路径但是并不一定能够成功。
# 实现
# JavaScript
// Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knight%27s_tour
class OpenKnightTour {
constructor (size) {
this.board = new Array(size).fill(0).map(() => new Array(size).fill(0))
this.size = size
}
getMoves ([i, j]) {
// helper function to get the valid moves of the knight from the current position
const moves = [
[i + 2, j - 1],
[i + 2, j + 1],
[i - 2, j - 1],
[i - 2, j + 1],
[i + 1, j - 2],
[i + 1, j + 2],
[i - 1, j - 2],
[i - 1, j + 2]
]
return moves.filter(([y, x]) => y >= 0 && y < this.size && x >= 0 && x < this.size)
}
isComplete () {
// helper function to check if the board is complete
return !this.board.map(row => row.includes(0)).includes(true)
}
solve () {
// function to find the solution for the given board
for (let i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.size; j++) {
if (this.solveHelper([i, j], 0)) return true
}
}
return false
}
solveHelper ([i, j], curr) {
// helper function for the main computation
if (this.isComplete()) return true
for (const [y, x] of this.getMoves([i, j])) {
if (this.board[y][x] === 0) {
this.board[y][x] = curr + 1
if (this.solveHelper([y, x], curr + 1)) return true
// backtracking
this.board[y][x] = 0
}
}
return false
}
printBoard (output = value => console.log(value)) {
// utility function to display the board
for (const row of this.board) {
let string = ''
for (const elem of row) {
string += elem + '\t'
}
output(string)
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# 参考
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2022/10/22, 22:03:41
